INTRODUCTION
On the contrary, with digital platforms that could be disconnected and viewed without human interaction, a disruptive coin has also been it on every level of the human experience, from how people interact amongst themselves within the confines of their own space, to buying and selling of goods all over the world. However, with this Information and Communication Technology (ICT) revolution, there is also a tsunami of issues, from data privacy and data security to cybercrime.
Thus cyber law is to be construed to impose criminal penalty to perpetrators, and to be apportioned on each party that has suffered cyber attack, and to protect the economy and the fundamental rights and interests of each party that has suffered cyber attack. Not only is it capable of helping to establish trust and confidence in virtual worlds, but also create ethical behavior in cyberspace. Because the framework of technological progress, net, is now too inflexible to be discussed, it should be viewed as flexible enough to deal with the questions generated by artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of things (IoT), and transnational storage and redistribution of data.
PRIVACY IN THE DIGITAL AGE :
Privacy is one of the most highly valued yet the most threatened of assets, in a digitally interlinked, global world. With the rise of the internet, social media and digital technologies, a variety of techniques for communication, interaction and information storage became available. Despite the remarkable pace of evolution, these advances have come with a loss of privacy, and it comes at the cost of convenience and connectivity.
However, as a result of a growing emphasis on privacy as a privacy issue, existing cyber law has been created thus far in order to defend the individual. Regulation (e.g., General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) which sets restrictions about the collection, use and sharing of data across Europe and the rest of the world. With the increasing sophistication of technology, and the advent of deep digital reality, serious attention must be paid to the importance of strong privacy protections in the internet era.
DATA PROTECTION LAWS :
In the modern digital marketplace, information is seen as one of the key assets. The fast growth of online tools has changed how firms run and people connect on the web, making information a main part in pushing new ideas and economic rise. But, with more personal and private info being created, gathered, and shared, protection of that data has become very important.
Importance of Data Protection –
Data security is key to keeping private life safe and sound in a well-linked world. In the digital market, personal info is often gathered by businesses for many reasons like selling, customer sorting, and service tailoring. Without good safety measures, this info can be misused or stolen which can lead to loss of privacy, identity theft, and money loss. Good rules on data protection make sure people keep control of their personal details while forcing firms to be responsible for its safety.
Global Data Protection Laws –
The waves of legislation in various countries and regions designed to protect personal data have been carried by the strong current of privacy reforms that began in the last decade and continue powerfully to this day, with perhaps the most significant having taken place in the European Union with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Enacted in 2018, GDPR is a great comprehensive law for all companies operating within the EU as well as those outside the EU dealing with the data of EU citizens. GDPR increased individual rights over personal information, including access, rectification, erasure, and data portability.
In 2020, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) was enacted to protect the privacy of Californians. Under the CCPA, Californians have the right to access, remove, and opt out of having their personal information sold. It’s a significant step toward providing better privacy protections in the United States, even if it isn’t on par with the GDPR.
India’s Data Protection Bill –
India also recognizes that strong data protection regulations are necessary. The Personal Data Protection Bill (PDPB), introduced in 2019, aims to provide a framework for the protection of personal data in India. This bill emphasizes data minimization, consent, transparency and the accountability of data handlers. It enables people to view, amend and delete personal data and obliges data controllers to have individuals’ express consent beforehand to collect it.
CYBER CRIME AND LEGAL PROTECTION :
Advancements in technology and the internet have made it easier for cybercrimes to emerge as criminals are taking advantage of how people now spend more time online. Cybercrimes are illegal activities conducted through computers and most digital devices, which include networks. Individuals, organizations, and nations are significantly threatened by such crimes. In order to fight these crimes and ensure the protection of digital spaces, laws around cyber crime have emerged.
Common Cybercrimes –
- Hacking – Hacking refers to gaining unauthorized access into one’s computer, system, or network without consent. Cybercriminals exploit loopholes in software and security protocols to steal confidential information, harm, or even disrupt processes.
- Phishing – Phishing is a social engineering style where criminals trick people into leaking personal information such as passwords, credit cards, or bank accounts. It is mostly done using emails, messages, or other forms of communication that masquerade as legitimate.
- Ransomware: Ransomware is a form of malware that locks or hijacks a target’s data. The encrypted data is restored only when the ransom is paid to the attacker. In recent times, it has gained notoriety as a form of cybercrime where cybercriminals infringe on companies and even people.

Legal Measures to Combat Cybercrimes –
Cybercrimes can take place in many manners, that is why many countries have drafted laws which penalize certain types of cyber activity. In India, there is an Information Technology Act, 2000, also known as the IT Act, which is particularly directed towards cybercrimes. This includes hacking, identity fraud, cyberstalking, and the transmission of offensive content. In addition, it includes cyber contracts, digital signatures, and sensitive personal data protection.
Real-Life Examples of High-Profile Cybercrime Cases
- WannaCry Ransomware Attack: The WannaCry ransomware attack represents one of the most catastrophic cyber incidents in recent history, occurring in May 2017. Approximately 200,000 computers were compromised across 150 nations, primarily exploiting weaknesses within the Windows operating system. Organizations, such as the UK’s National Health Service (NHS), were profoundly affected, experiencing locked systems and the loss of access to essential data. This attack not only underscored the exposure of organizations to ransomware threats, but it also illuminated the extensive scale at which cybercrimes can occur.
- Target Data Breach: In 2013, the retail powerhouse Target became the target of a significant cyberattack, wherein hackers infiltrated the systems and accessed the personal and financial details of over 40 million customers. This breach was largely due to inadequate cybersecurity measures, leading to severe financial repercussions and reputational harm for the company. Although this case exemplifies the critical need for strong security protocols, it also serves as a reminder that vigilance is necessary to combat cybercrimes, especially within the retail industry.
How Cyber Law Protects Individuals and Organizations –
Cyber law is a key tool to guard cybercrimes and the clients and the firms. IT Act legal regulations, for instance, provide the way to prosecute cybercriminals and the establishment of penalties for offenses like hacking, data theft, and online fraud. Besides, Cyber law secures that individuals who have been the victims of privacy or intellectual property rights violations have legal recourse online.
Cyber law assures that companies are in compliance with the rules about the protection of data and privacy. Cyber law is a way of ensuring that through data encryption, secure transactions, and breach notifications, sensitive corporate data and customer information are shielded from cyberattacks.
CHALLENGES IN CYBER LAW:
One of the most challenging and challenging tasks nowadays is the enforcement of laws related to cybercrimes. The global nature of the internet presents significant challenges to traditional legal systems, complicating the prosecution, and prevention of cybercrimes. Here, we explore some of the primary issues in cyber law enforcement.
Jurisdictional Issues –
The enactment of justice over the internet is very much problematic. Cybercrimes often involve multiple jurisdictions, with attackers operating from different countries, targeting victims in others. This makes it difficult to determine which country’s laws apply and where legal action should be taken.
For instance, an individual in one country could launch a cyberattack against an organization in another, leading to a complex web of legal issues. This problem is further exacerbated by the absence of consistent legal frameworks as some countries may have very strict and specific regulations compared to others that may have only weak enforcement.
Lack of Global Cooperation –
In spite of the need, national cooperation practicing of enforcing laws against cybercrimes is a challenge. Cybercrime knows no borders, yet international cooperation in enforcing cyber laws remains limited. While treaties like the Budapest Convention on Cybercrime have been established, not all countries are signatories, and varying laws and political climates hinder cross-border collaboration.
Tension Between Privacy and National Security –
Another challenge in cyber law enforcement is the tension between the need for privacy on the part of the individual on the one hand and the demand for national security on the other. Governments’ pursuits are mostly directed at access to individuals’ private data in the bid for potential hacking or the prevention of national security threats, meaning that the issue of surveillance and data privacy violations comes in. Regulations such as the USA PATRIOT Act and UKs Investigatory Powers Act are super broad on surveillance which is needed.
ROLE OF TECHNOLOGY IN PROTECTING PRIVACY AND DATA:
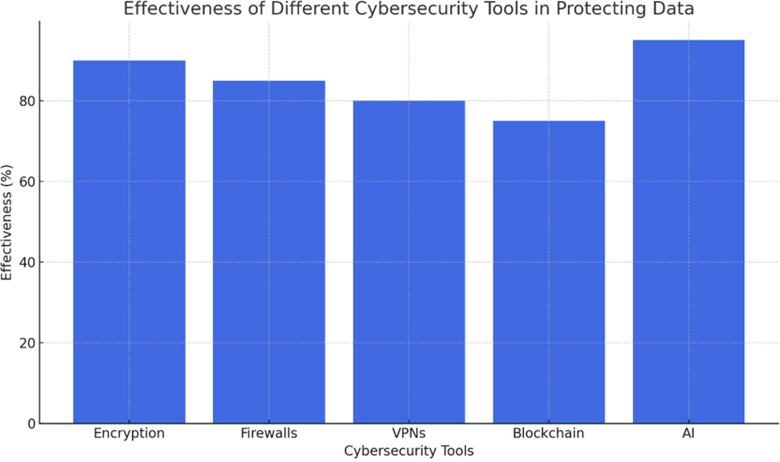
In the digital age, the importance of the personal and sensitive data is always increasing because the data can be attacked frequently. We can see how the technology is an essential factor here since it is through technology that the data are protected and their privacy well ensured. As the cyber threats are changing day by day, so also are the technologies and strategies created for the protection of the information. In this article we shall investigate how encryption, blockchain, AI, and other cybersecurity are being utilized for data protection and the impression of newly emerged technologies like IoT and quantum computing on the same.
Encryption and Blockchain –
- Encryption: Data encryption is the most effective tool to safeguard your information because no one would be able to access it. By converting plain text data into a scrambled version, encryption technology guarantees that only the persons with the right code can read the original text. Whether it be for encrypting data on the go (for example in online transactions) or for isolating singular nodes from a cloud service, encryption has always been a transformative concept in privacy-safe technological approaches.
- Blockchain: Blockchain, which was previously known only for being the underpinning technology behind the cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, has for some time now been gaining some interest and has been evaluated for the potential impact it can have on data protection. It relies upon decentralized ledgers as a substitute for centralized digital databases that are incapable of being tempered with or hacked.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) –
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a very innovative technology that has a wide range of use cases in data protection, mainly in the field of cyber security. AI-driven systems are capable of examining volume of data in the real-time mode to detect the anomalies which might indicate the breach or a possible threat. One of these methods, namely, machine learning algorithms that are a branch of AI, are more effective in locating patterns of dubious actions like phishing attacks or malware and can even act to solve these risks.
Cybersecurity Tools and Strategies –
- Firewalls: Firewalls serve as a defense mechanism that protects the internal network from untrusted external networks, like the internet. These gates are responsible for the monitoring and regulation of both the incoming and outgoing traffic. The cutting-edge firewalls, the so-called next-generation firewalls (NGFW), contain the functionality like intrusion detection and prevention, application awareness, and advanced threat protection.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): VPNs are used to link a network remotely and create an encrypted, secure connection to protect information during wireless communication. VPNs are indispensable for the secure transmission of data and especially when using the public Wi-Fi network. For this purpose, they are employed by people as well as organizations while browsing the internet and accessing remote servers.
Impact of Emerging Technologies –
- Internet of Things (IoT): The rapid progress of IoT tools—intelligent household products, wearable devices, and industrial sensors—has brought new privacy risks and cybersecurity challenges. Employing an encryption algorithm, secure communication mechanisms, and regular software upgrades, the security of IoT devices can be improved. In spite of that IoT technology at the present moment lacks a decent level of security, which means a high possibility of leading to cyber exploits.
- Quantum Computing: Quantum computing, a technology that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to perform calculations at speeds never seen before to break encryption, is a big disruptor in the traditional encryption methods. While quantum computing will be able to break widely used encryption algorithms such as RSA, quantum cryptography is one of the fields which is developing the countermeasures like quantum key distribution (QKD) allowing us to build such kind of encryption systems which are very difficult to break.
FUTURE TRENDS IN CYBER LAW :
The rapid development of technology has caused the emergence of many new threats, affecting cyber law. Quantum computing is the most difficult to deal with in terms of security of information, considering the potential to break the standard encryption mechanism. Thus, the software of this type should be developed with the security level to be correspondingly improved. First, it will be directed in the United States military and large scientific areas. Quantum-resistant cryptographic standards will need to be implemented in a timely manner, in
order to safeguard the existing legal frameworks from quantum computer attacks that will endanger the security of the systems.
The control over AI is another principal task. The AI systems, which depend much on their own intelligence for action and combine in decision-making processes, will be among the main issues that legal systems have to presuppose with reference to tethicality, accountability, and transparency.
The state of digital sovereignty and the trans-boundary movement of data are the ones that are of utmost relevance in the upcoming era of cyber rulemaking. There is increasing Globa Data Center for data storage and Sextant Technologies the vertex for the information to be locally processed and stored.
CONCLUSION:
Cyber law is an in-demand field today for gaining the necessary skills to run businesses and societies. The pace of technological development requires lawmakers to come up with new legal tools to face complex AI challenges, quantum computing, and cross-border data governance. The soundness, as well as the flexibility of laws, is something without which the individuals, organizations, and countries would be exposed to cyber risks. Instead of legislation only, a multi-stakeholder approach and raising individual awareness should be the cornerstones in the development of safe cyber areas. Through collaboration and being well informed, we can now safeguard our privacy as well as the informational security of the next generation in the digital world.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): https://gdpr.eu
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): https://oag.ca.gov/privacy/ccpa
- Information Technology Act, 2000 (India): https://www.meity.gov.in/content/information-technology-act
- Cybercrime and Law Resources:
- Budapest Convention on Cybercrime: https://www.coe.int/en/web/cybercrime/the-budapest-convention
- The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA): https://www.cisa.gov/cybersecurity
- AI Regulation and Ethics:
- AI and Ethics Research – European Commission: https://ec.europa.eu/digital-strategy/our-policies/european-ai-alliance_en
- AI and Law Overview – Stanford Law School: https://law.stanford.edu/ai- and-law/
- Cybersecurity Tools and Strategies:
- National Cyber Security Centre (UK): https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/
- Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) – Tools & Resources: https://www.cisa.gov/cybersecurity-tools
- Impact of Emerging Technologies (IoT, Quantum Computing):
- IoT Security – National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST): https://www.nist.gov/
- Quantum Computing and Data Security – MIT Technology Review: https://www.technologyreview.com/
- Data Privacy and Digital Sovereignty: https://ec.europa.eu/digital-strategy/our-policies/data-protection_en
- Cybercrime Case Studies (WannaCry, Target Data Breach):
- WannaCry Ransomware Attack – BBC News: https://www.bbc.com/news/technology-39916568
- Target Data Breach – US Federal Trade Commission (FTC): https://www.ftc.gov/data-breach-resources




