
Introduction
Climate change is accelerating, causing huge concerns for species around the world. Species have lost habitat, shifted their distribution, and disrupted their life cycles, all of which increase the risk of extinction. In reaction to these dangers, environmental law has evolved as an important tool for biodiversity conservation. This article investigates how climate change affects animals and the role of environmental law in mitigating these effects.
The Impact of Climate Change on Wildlife
Climate change has a major effect on wildlife by changing habitats, food availability, and the timing of natural processes. As global temperatures rise, coral reefs, wetlands, and Arctic regions suffer severe degradation. These changes undermine the delicate balance of ecosystems, resulting in the extinction of species that are unable to change quickly enough to changing circumstances.
Habitat Loss and Fragmentation
One of the most serious consequences of climate change for wildlife is habitat loss. Rising sea levels, greater wildfire frequency, and shifting precipitation patterns all contribute to 1 habitat loss and fragmentation. For example, polar bears are losing their sea ice habitats, which are essential for hunting seals, their principal food source. Similarly, amphibians and reptiles are highly vulnerable to temperature and moisture fluctuations, which can lead to population decreases.
Shifts in Species Distribution
Climate change also causes organisms to relocate to more suitable environments. However, this shift in distribution may result in conflicts with human activities such as agriculture and urbanization. Furthermore, species that are unable to migrate due to geographical or physical limitations risk extinction. The transfer of species into new places has the potential to destabilize current ecosystems by competing for resources with native species.
Disruption of Life Cycles
Natural events like breeding, migration, and hibernation are frequently timed to coincide with precise environmental cues. Climate change changes these cues, causing inconsistencies in the timing of certain events. For example, birds may arrive at mating grounds before food sources become accessible, resulting in lower reproductive success. Plants may also blossom earlier than usual, leaving pollinators with less food.

The Role of Environmental Law in Wildlife Protection
Environmental law plays a crucial role in addressing the challenges posed by climate change to wildlife. It provides a framework for the conservation of biodiversity, the protection of habitats, and the regulation of human activities that contribute to climate change. Key environmental laws and international agreements are instrumental in safeguarding wildlife from the impacts of climate change.
National Wildlife Protection Laws
National regulations are critical for protecting animals from the effects of climate change. In the United States, the Endangered Species Act (ESA) is an effective instrument for conserving species on the verge of extinction. The ESA compels federal agencies to consider the effects of climate change when making decisions affecting endangered species and ecosystems. Similarly, India’s Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 forbids hunting endangered species and controls activities that may destroy their habitats.
Protected Areas and Habitat Conservation
Protected places, including national parks, wildlife reserves, and marine sanctuaries, are crucial for preserving biodiversity in the face of climate change. Environmental laws frequently establish these protected areas, offering legal protection against activities that could harm habitats. For example, the construction of marine protected areas under the Marine Protection, Research, and Sanctuaries Act in the United States aids in the preservation of key ecosystems such as coral reefs, which are especially vulnerable to climate change.

International Environmental Agreements
Climate change is a global issue requiring international cooperation. Several international accords address the protection of wildlife and habitats in the context of climate change. The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) is an important international convention that seeks to protect biodiversity, encourage sustainable use of natural resources, and fairly distribute the advantages of genetic resources. The CBD encourages nations to include climate change issues in their national biodiversity strategy and action plans.
Another important international agreement is the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS). The CMS focuses on the conservation of migratory animals that cross international borders and are impacted by climate change. It fosters coordinated efforts among countries to conserve migratory routes and habitats, 3 assuring their survival.
The Role of Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation
Environmental law not only addresses the direct effects of climate change on animals, but it also contributes to climate change mitigation efforts. Environmental laws help to mitigate the overall impact of climate change on ecosystems and species by regulating greenhouse gas emissions, promoting renewable energy, and encouraging sustainable practices.
Climate change adaption measures are also essential for animal conservation. Environmental regulations can help to make adaptation strategies like restoring degraded habitats, creating wildlife corridors, and managing invasive species more effective. These measures assist species in coping with their changing habitat and increasing their resilience to climate change.
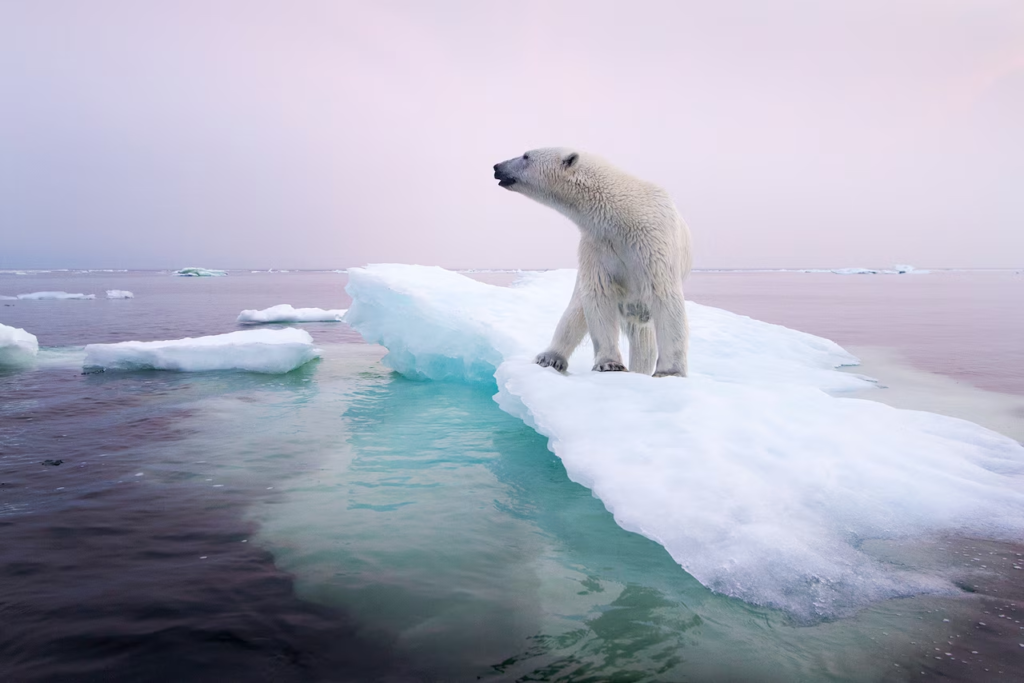

Challenges and Future Directions
Despite great advances in animal preservation under environmental legislation, some obstacles persist. Enforcement of environmental regulations is frequently inconsistent, especially in developing nations with little resources. Furthermore, the rapid rate of climate change necessitates ongoing revisions to legal frameworks to handle emerging hazards.
Balancing economic development with animal conservation is a significant task. Agriculture, mining, and energy production are all industries that frequently compete with wildlife conservation initiatives. Environmental rules must establish a balance between these competing interests, ensuring that commercial activities do not harm biodiversity.
Conclusion
Climate change poses enormous difficulties to wildlife conservation, but environmental law provides critical instruments for preserving biodiversity. Environmental law is crucial in minimizing the effects of climate change on wildlife because it regulates human activity, creates protected areas, and promotes international collaboration. As the effects of climate change worsen, it is critical that environmental laws evolve to meet these challenges, safeguarding the survival of the planet’s rich biodiversity for future generations.



1 thought on “Wildlife Conservation in the Face of Climate Change: The Role of Environmental Law ”