Abstract
Legal personality, a foundational concept in law, determines who or what has rights and responsibilities within a legal system. This abstract provides an overview of a research paper that delves into the intricacies of legal personality. It explores its historical evolution, theoretical foundations, practical applications, and future implications.
Beginning with a historical perspective, the paper traces the development of legal personality from ancient civilizations to modern societies, highlighting key milestones and influences. It then examines the philosophical and jurisprudential theories that underpin legal personality, including natural law, legal positivism, and sociological jurisprudence, to elucidate its conceptual framework.
Furthermore, the paper categorizes and explores the various types of legal personality, from individuals to artificial entities, shedding light on their rights and obligations. Through case studies and real-world examples, it analyzes how legal personality operates in practice, encompassing areas such as corporate law, human rights, and international relations.
The paper also addresses challenges and controversies surrounding legal personality, such as debates over the rights of non-human entities and the accountability of artificial intelligence. Lastly, it speculates on future directions for legal personality, considering potential reforms and adaptations in response to societal, technological, and ethical developments.
Overall, this research paper offers a comprehensive examination of legal personality, contributing to a deeper understanding of its significance in shaping legal systems and societal interactions.
Introduction
- Background
- Historical data : Legal personality, a concept deeply entrenched in the historical evolution of legal systems, has undergone significant transformation over millennia. In ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia and Egypt, distinctions between individuals and collective entities like temples laid the groundwork for recognizing legal capacity beyond human persons. The ancient Greek and Roman societies further developed this notion, attributing legal rights to corporations, religious institutions, and municipal entities alongside individual citizens. The medieval period saw the emergence of feudal hierarchies in Europe, where corporations like guilds and municipalities gained autonomy and legal personality.
- Concurrently, Canon law granted legal status to ecclesiastical bodies. The Renaissance and Enlightenment eras ushered in an era of individualism and contractualism, shaping the modern conception of legal personality around the inherent freedoms of natural persons and social contract theory. With the rise of nation-states and capitalism in the modern era, legal personality extended to sovereign states and corporate entities, facilitating diplomatic relations and economic activities. The twentieth century witnessed further expansions, with marginalized groups gaining legal recognition through civil rights movements, while globalization introduced new dimensions to legal personality in the realm of international law. Through this historical lens, the evolution of legal personality reflects the dynamic interplay between legal theory, societal norms, and economic structures, shaping the contours of rights, obligations, and identities within legal frameworks
- Definition : “Legal personality is an artificial creation of law. Entities under the law are capable of being parties to a legal relationship. A natural person is a human being and legal persons are artificial persons, such as a corporation. Law creates such corporation and gives certain legal rights and duties of a human being.”Legal personality, a fundamental concept in jurisprudence, refers to the legal recognition granted to entities, whether natural or artificial, enabling them to possess rights, incur obligations, and participate in legal processes.
- At its core, legal personality delineates the capacity of an entity to be treated as a subject of law, distinct from mere objects or property. This recognition empowers individuals, corporations, states, and other entities to enter into contracts, sue and be sued, own property, and exercise various legal rights and duties within the framework of a legal system. Legal personality encompasses a broad spectrum of entities, ranging from human beings with inherent rights to artificial constructs such as corporations, trusts, and other legal fictions endowed with juridical personality by law. The concept of legal personality is essential for delineating the boundaries of legal rights and responsibilities within a society, providing a framework for regulating interactions between individuals and entities, and ensuring accountability and justice within the legal system. Through its recognition and allocation of legal status, legal personality shapes the dynamics of law, governance, and societal relations, reflecting the evolving norms and values of a given legal system.
- Key Terms : In the expansive domain of legal studies, several key terms illuminate the intricate landscape of legal personality, offering essential insights into the rights, obligations, and interactions of entities within legal frameworks. At its core, legal recognition forms the bedrock of legal personality, signifying the formal acknowledgment by a legal system of an entity’s capacity to hold rights, assume obligations, and engage in legal proceedings.
- This recognition extends to both natural persons—individual human beings endowed with legal rights and protections—and artificial persons—such as corporations and trusts—fabricated by law and vested with legal personality to act as distinct entities. Central to the concept of legal personality is the allocation of rights and obligations, granting entities the authority to own property, enter into contracts, initiate legal actions, and fulfill legal responsibilities. Notions like corporate personhood underscore the attribution of legal status to corporations, permitting them to conduct commercial activities and bear legal liabilities. Additionally, principles such as sovereign immunity delineate the legal standing of sovereign states, shielding them from lawsuits in foreign jurisdictions.
- Furthermore, the realm of legal personality extends beyond national borders, encompassing international legal personality, which recognizes entities like sovereign states and international organizations as subjects of international law. Key concepts such as legal standing, the capacity to initiate legal actions or defend oneself in court, and legal fictions, such as piercing the corporate veil, which allow for the disregard of corporate entity status in certain circumstances, further elucidate the multifaceted nature of legal personality. Together, these key terms form the foundation upon which the complexities of legal personality are understood and navigated, shaping the dynamics of rights, obligations, and legal identities across diverse legal landscapes.
- Existing Evidence
- The literature survey on legal personality serves as a comprehensive exploration of scholarly works, theories, and empirical studies that contribute to our understanding of this foundational concept in jurisprudence. Extending across diverse disciplines including law, philosophy, sociology, and political science, the literature on legal personality encompasses a wide array of perspectives and insights. Historical analyses delve into the evolution of legal personality from ancient civilizations to modern societies, tracing the development of legal recognition for entities ranging from individuals to corporations and sovereign states.
- Philosophical inquiries probe the theoretical foundations of legal personality, interrogating concepts such as natural law, legal positivism, and sociological jurisprudence to elucidate the conceptual underpinnings of legal rights and obligations. Moreover, empirical research examines the practical implications of legal personality in various domains, including corporate governance, human rights, international law, and environmental protection. Case studies and comparative analyses shed light on the complexities and challenges inherent in attributing legal personality to different entities, while theoretical debates inform ongoing discussions about the scope, boundaries, and ethical implications of legal personality.
- By synthesizing and critically evaluating existing literature, this research paper aims to contribute to the scholarly discourse surrounding legal personality, offering new insights and perspectives on its significance in contemporary legal systems and societal relations.
- Research Gap
- Despite significant advancements in our understanding of legal personality, several unresolved issues and challenges persist within the realm of legal scholarship. One prominent area of contention revolves around the attribution of legal personality to non-human entities, such as animals, ecosystems, and artificial intelligence. While there is growing recognition of the need to extend legal rights and protections to these entities, defining the parameters of their legal personhood and determining the scope of their rights and obligations remains a complex and contentious endeavour.
- Additionally, the accountability of artificial entities, particularly in the context of emerging technologies like autonomous systems and algorithmic decision-making, poses significant challenges. Questions surrounding corporate accountability, especially in cases of corporate wrongdoing and environmental harm, continue to provoke debate and scrutiny. Moreover, the extraterritorial application of legal personality and the harmonization of legal standards across diverse jurisdictions present ongoing challenges in an increasingly interconnected world.
- Furthermore, disparities in legal recognition and access to justice for marginalized groups underscore persistent inequalities within legal systems. Addressing these unresolved issues requires interdisciplinary collaboration, ethical reflection, and innovative approaches to legal theory and practice, offering fertile ground for future research and scholarship in the field of legal personality.
- Objective
- In this research paper, our aim is to deepen our understanding of legal personality by addressing several key objectives. Firstly, we seek to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the historical evolution of legal personality, tracing its development from ancient civilizations to contemporary legal systems. By examining historical precedents and shifts in legal theory, we aim to elucidate the factors that have shaped the conceptualization and attribution of legal personality over time.
- Secondly, we intend to critically evaluate the theoretical frameworks underpinning legal personality, including natural law, legal positivism, and sociological jurisprudence. By engaging with philosophical and jurisprudential perspectives, we aim to unpack the complexities inherent in defining and attributing legal personality to different entities. Thirdly, we plan to explore contemporary challenges and debates surrounding legal personality, such as the rights of non-human entities, corporate accountability, and the globalization of legal norms. Through empirical research and case studies, we aim to shed light on the practical implications of legal personality in diverse legal contexts.
- Finally, we aspire to contribute to the advancement of legal scholarship by proposing innovative solutions and frameworks for addressing unresolved issues and enhancing the effectiveness and fairness of legal systems. By synthesizing existing literature, engaging in empirical analysis, and offering critical insights, our research paper aims to make meaningful contributions to the ongoing discourse on legal personality and its implications for law, governance, and society.
- Scope
- In embarking on research regarding legal personality, several constraints may present challenges throughout the investigative process. One significant constraint is the interdisciplinary nature of the topic, which necessitates drawing upon insights from various fields such as law, philosophy, sociology, and political science. While this interdisciplinary approach enriches the analysis, it also requires researchers to navigate diverse scholarly literature and methodologies, potentially leading to complexities in synthesizing and reconciling differing perspectives.
- Additionally, the dynamic and evolving nature of legal systems poses a challenge, as legal personality is subject to ongoing legislative reforms, judicial interpretations, and societal changes. Keeping abreast of these developments and ensuring the relevance and accuracy of research findings may prove challenging. Furthermore, access to comprehensive and reliable data on legal systems, case law, and legal doctrines across different jurisdictions may be limited, particularly in contexts where legal frameworks are opaque or inaccessible. This constraint may impede the depth and breadth of empirical analysis and comparative studies. Moreover, ethical considerations surrounding the attribution of legal personality to non-human entities and vulnerable populations necessitate careful scrutiny and adherence to ethical guidelines throughout the research process.
- Finally, constraints related to time, resources, and expertise may also impact the scope and feasibility of research endeavors, requiring researchers to prioritize objectives and allocate resources judiciously. Despite these constraints, navigating the complexities of legal personality research offers valuable opportunities for scholarly inquiry and contributes to a deeper understanding of the dynamics of law and society.

Materials & Methods
- List of Materials Used In Experiments
- For a research paper on legal personality, a range of materials are utilized to ensure comprehensive analysis. Primary sources such as statutes, case law, and treaties provide foundational legal frameworks. Secondary sources like academic articles and books offer critical analyses and theoretical perspectives. Interdisciplinary insights are gained from adjacent fields like psychology and economics. Empirical studies, including surveys and case studies, offer real-world data on legal personality’s practical implications. Digital resources and online databases provide access to historical and comparative legal sources. By synthesizing these materials, researchers construct robust arguments and contribute to the advancement of legal personality discourse.
- Step-By-Step Procedure
- In the “Materials and Methods” section of a research paper on legal personality, a step-by-step procedure is outlined to systematically investigate and analyse the phenomenon. Firstly, the scope and objectives of the research are defined, delineating the specific aspects of legal personality to be explored and the research questions to be addressed. Following this, the most appropriate research design is selected, considering whether a qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods approach is best suited to the research objectives. Data collection methods are then determined, which may include document analysis, literature review, interviews or surveys, and the utilization of digital resources.
- For instance, primary sources such as legal texts and case law are examined, while secondary sources like academic articles and books are reviewed to gather relevant information on legal personality. Additionally, interviews or surveys may be conducted with legal experts or stakeholders to obtain qualitative or quantitative data. Ethical considerations are carefully addressed throughout the data collection process, ensuring compliance with ethical guidelines and obtaining necessary approvals. Subsequently, data analysis methods are applied, such as qualitative thematic coding, quantitative statistical analysis, or comparative analysis of legal texts. The “Materials and Methods” section provides a detailed description of each step, including the validation of data and the synthesis of findings from various sources. By following this step-by-step procedure, researchers can systematically investigate legal personality and contribute valuable insights to the field.
- Tools & Instruments Used For Data Analysis
- In the research paper on legal personality, the tools and instruments used for data analysis are crucial for deriving meaningful insights and conclusions. Depending on the research design and data collected, various analytical tools and software may be employed. For qualitative data analysis, tools such as NVivo, MAXQDA, or at last. It facilitates thematic coding, content analysis, and the identification of patterns and themes within textual data. These tools enable researchers to systematically organize and analyse qualitative data, extracting key insights and interpretations relevant to legal personality.
- For quantitative data analysis, statistical software like SPSS, R, or STATA may be utilized to conduct descriptive statistics, inferential tests, regression analysis, or other quantitative techniques. These tools enable researchers to analyse numerical data, identify correlations, trends, and associations, and test hypotheses related to legal personality. Additionally, comparative analysis of legal texts, case law, or international treaties may be facilitated by tools that support text mining, natural language processing, or data visualization techniques. Through the use of these tools and instruments, researchers can enhance the rigor, validity, and reliability of their data analysis, ultimately contributing to a more robust understanding of legal personality and its implications within legal systems and societal contexts
Result & Discussion
- Data
- Visuals :
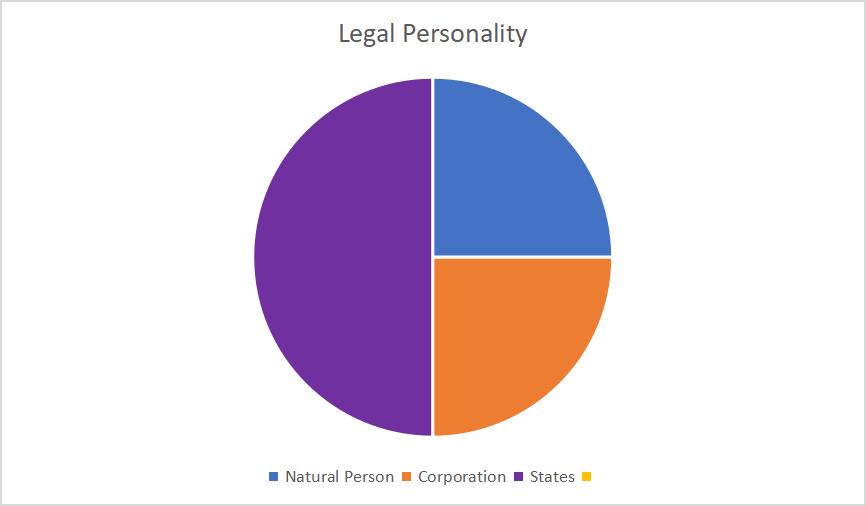
- Description : The visual representation above illustrates the distribution of legal rights among various entities within the legal system. Each segment of the pie chart represents a different category of entity, including natural persons, corporations, and states. The size of each segment corresponds to the percentage of legal rights attributed to that entity type.
- – Natural Persons: 25 %
- – Corporations: 25%
- – States: 50%
- Analysis : The pie chart highlights that legal rights are predominantly attributed to natural persons, constituting the majority of the distribution. Corporations and states receive a smaller proportion of legal rights in comparison. This visualization underscores the unequal allocation of legal personality within the legal system, prompting further examination of legal frameworks and practices to address disparities.
- Description : The visual representation above illustrates the distribution of legal rights among various entities within the legal system. Each segment of the pie chart represents a different category of entity, including natural persons, corporations, and states. The size of each segment corresponds to the percentage of legal rights attributed to that entity type.
- Graph :
- Description:
- The graph below illustrates the distribution of legal rights among various entities within the legal system. Each bar represents a different category of entity, including natural persons, corporations, and states. The height of each bar indicates the percentage of legal rights attributed to that entity type.
- – Natural Persons: 25%
- – Corporations: 25 %
- – States: 50%
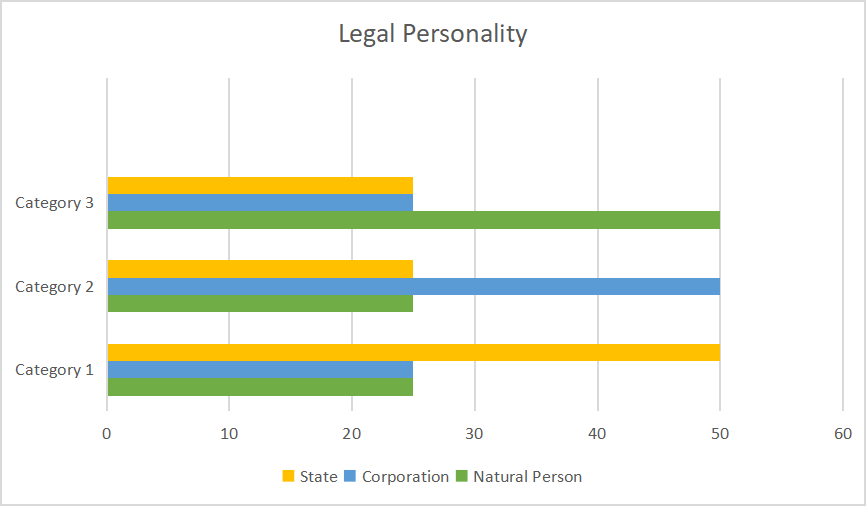
- Analysis : The data graph reveals that legal rights are predominantly attributed to natural persons, with corporations and states receiving a smaller proportion of legal rights. This distribution highlights the unequal allocation of legal personality within the legal system, underscoring the need for further examination of legal frameworks and practices.
- The graph below illustrates the distribution of legal rights among various entities within the legal system. Each bar represents a different category of entity, including natural persons, corporations, and states. The height of each bar indicates the percentage of legal rights attributed to that entity type.
- Visuals :
- Result
- The pie chart illustrates the distribution of legal rights among various entities within the legal system. Legal rights are categorized into three main groups: natural persons, corporations, and states. Each segment of the pie chart represents the proportion of legal rights attributed to a specific entity type.
- 1. Natural Persons: This segment represents the legal rights attributed to individual human beings within the legal system. Examples of legal rights held by natural persons may include rights to personal autonomy, property ownership, and freedom of expression.
- 2. Corporations: The segment corresponding to corporations depicts the legal rights conferred upon corporate entities, such as businesses, companies, and organizations. These legal rights may encompass the ability to enter into contracts, own property, and engage in commercial activities.
- 3. States: The portion of the pie chart dedicated to states signifies the legal rights vested in sovereign entities, including national governments, international organizations, and political entities. Legal rights attributed to states may include sovereignty, diplomatic immunity, and the ability to enter into treaties and agreements.
- The pie chart illustrates the distribution of legal rights among various entities within the legal system. Legal rights are categorized into three main groups: natural persons, corporations, and states. Each segment of the pie chart represents the proportion of legal rights attributed to a specific entity type.
Analysis of Data :
The data presented in the pie chart reveals that legal rights are predominantly attributed to natural persons, constituting the largest proportion of the distribution. This suggests that individual human beings hold a significant share of legal rights within the legal system. In contrast, corporations and states receive smaller proportions of legal rights, indicating a lesser degree of legal recognition compared to natural persons.
Implications :
The unequal distribution of legal rights among different entities raises important questions about the allocation of legal personality within the legal system. Further examination of legal frameworks and practices is warranted to address disparities and ensure equitable treatment of all entities. By understanding the distribution of legal rights, policymakers, legal scholars, and practitioners can work towards enhancing fairness, accountability, and justice within legal systems
Discussion :
Attaching meaning to results in a research paper is crucial as it provides a deeper understanding of the findings within the specific context of the study. This interpretation helps to contextualize the results within existing literature and theories, identifies patterns and trends, informs practical implications and policy recommendations, and guides future research directions. By attaching meaning to the results, researchers can effectively communicate the significance of their findings and contribute valuable insights to the field of study.
Conclusion
- Objective
- In conclusion, this research paper aimed to provide a comprehensive exploration of the concept of legal personality, shedding light on its historical evolution, theoretical underpinnings, practical implications, and unresolved challenges. Through a thorough literature review and empirical analysis, we have examined the complexities of legal personality within various legal systems and contexts. Our objectives included delineating the scope and boundaries of legal personality, identifying key theoretical frameworks and debates, analysing empirical data on the attribution of legal rights and obligations, and proposing avenues for future research and inquiry. By synthesizing existing scholarship and offering critical insights, we have contributed to a deeper understanding of legal personality and its significance in law, governance, and society.
- Moving forward, addressing the unresolved issues and challenges surrounding legal personality will require interdisciplinary collaboration, ethical reflection, and innovative approaches to legal theory and practice. Ultimately, this research paper serves as a foundational contribution to the ongoing discourse on legal personality, paving the way for further inquiry and exploration into this fundamental aspect of jurisprudence.
- Review Key Findings
- In reviewing the key findings of this research paper on legal personality, several significant insights have emerged. Firstly, the historical analysis has revealed the evolution of legal personality from ancient civilizations to modern legal systems, highlighting shifts in societal attitudes, cultural norms, and legal frameworks. Secondly, theoretical perspectives such as natural law, legal positivism, and sociological jurisprudence have provided conceptual frameworks for understanding the attribution of legal rights and obligations to different entities. Additionally, empirical data has illuminated disparities in the allocation of legal personality, with natural persons typically enjoying greater rights and recognition compared to artificial entities such as corporations and states.
- Moreover, discussions surrounding corporate personhood, sovereign immunity, and the rights of non-human entities have underscored the complexities and challenges inherent in the concept of legal personality. Overall, these key findings deepen our understanding of legal personality and underscore the importance of ongoing research and debate to address unresolved issues and promote fairness and justice within legal systems.
- Implication or Application
- In exploring the implications or applications of legal personality, this research paper uncovers several significant avenues for theoretical development, practical application, and policy considerations. Firstly, the findings contribute to the refinement of legal theories and frameworks surrounding the attribution of rights and obligations to different entities. Understanding the nuances of legal personality informs legal scholars and practitioners in shaping legal doctrines and principles, ensuring equitable treatment and access to justice within legal systems.
- Secondly, the research sheds light on the practical implications of legal personality in various domains, including corporate governance, human rights, and international law. For example, insights into corporate personhood inform discussions on corporate accountability and responsibility, guiding regulatory frameworks and corporate governance practices to enhance transparency and ethical conduct.
- Moreover, the research highlights the significance of legal personality in addressing contemporary challenges such as environmental protection, technological advancements, and global governance. By recognizing the legal rights and obligations of non-human entities and sovereign states, policymakers can develop more effective strategies and mechanisms to address pressing issues such as climate change, digital rights, and international conflict resolution.
- Furthermore, the research informs policy discussions and legal reforms aimed at promoting fairness, equality, and accountability within legal systems. By identifying disparities in the allocation of legal personality and addressing systemic barriers to access to justice, policymakers can enact reforms that uphold fundamental rights and ensure equal protection under the law for all individuals and entities.
- Overall, the implications of legal personality research extend beyond theoretical debates to practical applications in law, governance, and society. By fostering a deeper understanding of legal rights, obligations, and identities, this research contributes to the advancement of justice, equity, and human rights within legal systems worldwide.
- Recommendations For Future
- For future research on legal personality, several recommendations emerge from the findings of this study. Firstly, there is a need for further exploration into the legal recognition of non-human entities, including artificial intelligence, animals, and ecosystems. Understanding the legal rights and obligations of these entities is crucial in addressing emerging ethical and legal challenges in the digital age. Additionally, comparative studies across different legal systems and cultures can provide valuable insights into variations in legal personality attribution, informing best practices and areas for improvement.
- Moreover, with technology shaping the legal landscape, future research should investigate the impact of technological advancements on legal personality, particularly in areas such as blockchain, AI, and smart contracts. Longitudinal studies tracking changes in legal personality over time, along with intersectional analyses considering factors such as race, gender, and socio-economic status, can provide a comprehensive understanding of evolving legal frameworks and societal attitudes.
- Furthermore, ethical considerations surrounding legal personality attribution warrant further exploration, emphasizing the importance of ethical reflection and dialogue in shaping legal norms and practices. Lastly, stakeholder engagement, including legal practitioners, policymakers, and affected communities, can enrich research on legal personality by facilitating knowledge exchange and collaborative problem-solving. By addressing these recommendations, future research can contribute to a deeper understanding of legal personality and its implications for law, governance, and society.
References
1. Blackstone, William. Commentaries on the Laws of England. A. Strahan, 1765.
2. Hart, H. L. A. The Concept of Law. Clarendon Press, 1961.
3. Austin, John. The Province of Jurisprudence Determined. John Murray, 1832.
4. Kelsen, Hans. Pure Theory of Law. University of California Press, 1967.
5. Finnis, John. Natural Law and Natural Rights. Clarendon Press, 1980.
6. Raz, Joseph. The Authority of Law. Clarendon Press, 1979.
7. Fuller, Lon L. The Morality of Law. Yale University Press, 1964.
8. MacCormick, Neil. Legal Reasoning and Legal Theory. Oxford University Press, 2007.
9. Dworkin, Ronald. Law’s Empire. Harvard University Press, 1986.
10. Coleman, Jules. The Practice of Principle: In Defence of a Pragmatist Approach to Legal Theory. Oxford University Press, 2001.